PENGUNAAN AMALAN SAINS SUKAN DALAM LATIHAN FIZIKAL
UNTUK PEMAIN-PEMAIN PETANQUE.
Telah menjadi tanggapan sebahagian pemain dan peminat petanque beranggapan di negara ini bahawa sukan petanque ini adalah amat mudah dan tidak memerlukan apa-apa maklumat dan latihan yang lain seperti amalan dalam sukan teras yang ada di Malaysia. Datang bawa bola 3 biji , buat point, shoot dan lawan sesama sendiri. Dalam kem-kem latihan pun sukar untuk melihat satu sistem yang menyeluruh penggunaan aplikasi sains sukan. Pernah saya ditegur apa perlunya saya melakukan amalan latihan dynamic warming up semasa MASUM 2013 kepada pasukan UMP. Saya diam saja. Bagi saya dengan keadaan suasana seperti itu, soalan itu tak perlu di jawab ketika itu. Biarlah masa dan keputusan perlawanan yang akan menjawabnya nanti. Pemain-pemain dalam sukma sekalipun begitu berat dan kelihatan mahu membantah untu
Sports
science related to the application of science in physical activities and
sports. Sports today have the scientific and systematic approach to ensure that
the athlete's performance could be improved. Understanding of some science
disciplines in sports such as anatomy , physiological , biomechanical , sports
psychology , sports management and training methods believed to help the
coaches to improve the knowledge in terms of coaching and help the athletes to
improve their performance to the optimum.
PHYSICAL TRAINING METHODS 7.1 ( 2 hours)
Owned outstanding achievements of athletes now reflects the depth of knowledge
and skills as a result of the rules of training. New rules , the result of
scientific research has enriched the theory and training methods. Training
methods applied in accordance with the type of sport and the needs of athletes
, thus allowing the athlete to achieve optimum fitness and success.
Physical training methods can be classified according to the use or need energy
systems such as :
- Aerobic Training Methods .
- Anaerobic Training Methods .
AEROBIC TRAINING METHODS 7.1.1
Aerobic exercise involves the recruitment, transportation and use oxygen
efficiently. Aerobic exercise can improve the body's capacity to produce ATP
through the breakdown of carbohydrates and fats stored in the body . Here is
the proposed training methods that can be used to increase aerobic capacity :
- Slow Distance ( LSD )
- Fartlek
- Interval Distance
7.1.1.1 Slow Distance Training
Slow distance training methods practiced by a marathon runner or long distance
runner . The main objective of this training is to build cardiorespiratory
fitness and increase aerobic endurance . The main aspect of this training is
emphasized in the distance and not speed. Ataujauh longer one can run
continuously, then the effect is even better for the cardiovascular system .
Slow distance training can reduce pressure on the cardiovascular and
respiratory systems are good for the entire adaptive resilience . Through this
method, the athlete can do at low intensity , for example, between 60 % to 80 %
of maximum heart rate . For adolescent athletes , training heart rate is above
160 beats per minute .
Fartlek Training 7.1.1.2
Fartlek or speed play method was first introduced in Sweden . Fartlek training
is a training method diversifying running speed . The objective of this
exercise is to increase cardiovascular endurance and muscular endurance . This
exercise can be done on the slopes of a hill, on the beach , climbing up the
stairs , in the open or on the track . Land surface conditions multifaceted and
different locations can give pleasure to the athletes. However, the security
aspects should be taken to avoid injury during training.
Training patterns are not concerned with the specific distance or time .
Freedom is given to the athlete to determine the appropriate variabellvariabel
with training such as distance , time and duration of fatigue began to be felt
by the athletes . During a training run , the practice of measuring the pulse
rate should a concern . This training can be regarded as interval training not
introduced at the end of Formal and general preparation phase until the
beginning of the preparation phase specific .
Here is a proposal for a Fartlek training session :
• Warm up for 5 to 10 minutes.
• Running fast in a constant state as far as 1 to 1.5 km .
• Brisk walking for 5 minutes.
• Jog alternating between the sprint distance of 60 to 70 meters up began to
feel tired .
• Running fast as far as 175 to 200 meters .
• Run fast for 1 minute .
• Run a few laps in his recovery .
•
Figure 1 Activities Fartlek .
7.1.1.3 Pause distance
Interval training was first introduced in Germany by Dr . Woldmar Gerschler and
Hans Reindell in the early 1930s. Jedajarakjauh training is a method of
scientific training with interval work and rest intervals . Apart from
improving the cardiovascular system and muscle endurance , exercise can improve
agility, flexibility, coordination , strength and speed.
Activities carried out over and over in a short time and there is a rest period
between each repetition . Variables such as exercise intensity , number of
repetitions , number of sets, rest intervals , the type and frequency of
training activities can be manipulated according to the athlete's ability and
objectives of the program .
For long-distance interval training , interval ratio of work to rest interval
is between 1 : ½ to 1:1 depending on the distance run or a mas taken to finish
a race . Examples are as follows :
• Running time = 20 minutes of break time
o Rest time = 10 minutes
o The ratio of jobs to pause pause interval = 1 : ½
• Running time = 5 minutes
o Time interval = 5 minutes
o work kepadajeda rest pause ratio = 1:1
The proposed replay is 2 to 3 repetitions for longer distances and between 3 to
4 repetitions for distances less than 800 meters for a one-time run. Meanwhile,
the proposed set is he similar to the number of repetitions , and rest between
sets is determined by the pulse rate when the pulse rate dropped to 120 beats
per minute , then started the second set .
Table 1 Proposed interval training
activities Run
Doing exercise intensity within 1500 meters race
Pause Work 8 minutes
Rest Pause 4 minutes
Work Rest ratio 1 : ½
Repetitions and sets 3 times x 2 sets
Rest Pause Activities Walking active
Pause Rest Between Sets When the heart rate back to 120 DSM set started
7.1.2 . METHODS Anaerobic Exercise
Anaerobic training methods are training methods that will enhance the ability
of anaerobic capacity to work efficiently and effectively without oxygen .
Anaerobic exercise can help energy production for activities that require
immediate energy like running 60 meters and 100 meters , close distance
swimming events and shot put . Anaerobic training methods are only able to
accommodate high intensity training for approximately one minute only.
Anaerobic training can help athletes improve the ability of the body to quickly
rebuild ATP during the rest of the work. The objectives of this training is to
enhance the components of fitness such as speed, strength , endurance, power
and agility . Several types of training are often used and are classified in
anaerobic training are:
• Interval training Short Range
• Medium Distance Interval Training
• Recurrent Acceleration Training
• plyometric training
• Training load
7.1.2.1 Interval training Short Range
Behavior of interval training procedures for short-haul and medium-haul pause
is no different than long-distance interval training . If the distance interval
training much emphasis on increasing aerobic power , interval training short
and medium-haul pause focused on the anaerobic capacity .
In the near distance interval training , primary energy system is the ATP -PC-
LA , a combination of anaerobic energy systems and anaerobic lactic alaktik ,
depending on the distance , time and intensity of the behavior of jobs . Higher
work intensity for the duration of the behavior of shorter more dominanlah
alaktik anaerobic energy system . The table below shows the implementation of
the guidelines close interval training .
Table 2 : Interval training guidelines close
Running distance 80-200 meters
Running time 10-30 seconds
Training intensity 85-95 %
Rest time between repetitions of 40-90 seconds
When rest time between sets pulse rate down to 120 pulses per minute
Pause ratio of work : rest interval between repetitions 1 : 3 to 1 : 4
Total sets per exercise session 3 to 6 sets
Applications annual training periodization training in the preparatory phase
End specifically , during the pre- competition phase and in the early phase of
the competition
All appropriate sport sports golf , tennis , athletics ( sprint and distance
swimming close.
7.1.2.2 Medium Distance Interval Training
Interval training middle distance focus on improving anaerobic lactic energy
system or simply system LA . Rest between repetitions and rest between sets
will train the muscles to produce ATP by anaerobic very quickly in addition to
the phase delay fatigue. Thus muscles can be involved in anaerobic work for
longer periods of time . In addition, this exercise also trains the muscles to
work better though blood lactate content is high . The table below shows the
implementation guidelines moderate distance interval training .
Table 3 : Interval training guidelines medium-range
Running distance 300-600 meters
Running time 40-90 seconds
Training intensity 70-80 %
Rest time between repetitions of 80 seconds to 3 minutes
When rest time between sets pulse rate down to 120 pulses per minute
Pause ratio of work : rest interval between repetitions 1 : 2
Total sets per exercise session 3 to 5 sets
Periodization training applications in annual training specific During the
preparation phase . Continued for endurance -based sports
All appropriate sport sports golf , tennis , athletics ( middle distance events
) and medium distance swimming long distances .
7.1.2.3 Training load
Weight training is a training program based on the use of strain as dumbbell ,
weights and multi- gym machine for either muscle fitness to improve strength ,
power or endurance . Burden and repetition of work depends on the objectives of
the exercise .
At principally high burden of 80 % to 90% of the maximum load that can be
lifted once only or 1 RM ( Repetition Maximum ) with little repetition increase
muscle strength . While low loadings ( < 50% of 1 RM ) with a lot of
repetition ( l0 to 30 times ) increase muscle endurance .
Weight training involves muscle contraction isometric , isotonic and isokinetic
.
• Isometric Exercise
Isometric means the power generated but not muscle size change. Muscle
contraction is statically. This means that when the exercise is done , the
muscles involved contract without shorten or lengthen. Joint angle does not
change. For example , when someone pushes an object that does not move like a
push din ding with elbow bent .
• Isotonic Exercise
Isotonic exercises are also known as dynamic muscle contraction or concentric
contraction . Concentric means the muscles involved will shorten during exercise
performed . Muscle contraction will produce consistent pressure against a
constant resistance . For example , using weights and dumbbell training .
• Training isokinetic
Isokinetic training is usually done using a machine . This training is very
effective because the maximum pressure produced by muscle during shorten is
consistent speed on the maximum angle of joint movement . In this exercise, the
load or resistance is automatically adjusted to the force exerted by the muscle
- oto1 . This produces a consistent force . Although the contraction is
concentric isokinetic and isotonic shorten the muscle , but the two are not the
same.
Maximum pressure generated during maximum joint movement but did not occur
during isotonic contraction . Machines used for training , including Cybex
isokinetic and Lido .
In performing weight training , it is important for an athlete to adapt to a
more specific activity at the level of specialization . At this stage , the
development of muscle fitness is specific to the trained muscle groups . The
workload was gradually developed to be added systematically to increase muscle
strength and endurance while avoiding injury to the muscles and ligaments.
The concept of maximum repetitions should be known for largest weight training
. RM is the number of repetitions that can be lifted by maksirnum performer of
a burden to the muscle or muscle groups involved are not able to continue
working ( temporary muscular failure ) .
Guide training load :
• Training shall be conducted based on the concept of load intensity , sets and
repetitions.
• To build muscle strength , weight starter is a sub- minimum , which is about
80% to 100 % by weight maximum capacity with low repetitions ( 1 to 3
repetitions ) .
• To build endurance, weight of the load is 20 % to 80 % of its maximum weight
with high repetitions ( 10 to 30 repetitions ) .
• To build power , weight load is between 50 % to 80 % by weight maximum
capacity with moderate repetitions ( 5 to 10 repetitions ) .
• When the pulse rate decreased and reached 120 beats per minute , participants
will begin the next set .
• Coaches should take into account the different recovery rates between
participants who underwent training .
Table 4 : User training burden
Physical components of Deuteronomy
Set Maximum Intensity Rest
Maximum strength Rs 3-4 1-2 2-5 minutes 95-100%
Strength 3-6 3-4 85-90 % RM 2-5 minutes
Hypertrophy of Rs 2-4 8-12 65-80 % 30-90 seconds
Muscle endurance Rs 20-50 15-45 30-60% 2-4 seconds
Adaptation Anatomy 20-25 RM 2-4 50-60 % 60-90 seconds
7.2 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND Exercise Physiology
MAIN BODY SYSTEM IN SPORT ( 1 hour )
Capabilities and individual performance in a sport depends on how his body can
adapt to the vigorous training . Several body systems combine to receive
further training and adapting to the training received in accordance with the
nature and needs of sport . Among these systems , five key system acts directly
in the sports of the skeletal system , muscular system , cardiorespiratory
system , the nervous system and energy system . As such , it is necessary for a
coach to know and understand these systems briefly in helping him become a good
coach , and subsequently apply this knowledge in training .
7.2.1 SYSTEM FRAMEWORK
Skeletal system give shape to the human body . Framework can serve as a strong
supporter and protector of other organs in the human body . There are about 206
pieces of bones of different shapes and sizes in the human body . Apart from
the skeletal system is also supported by other structures such as ligaments ,
tendons and cartilage.
Figure 2 shows the skeleton of the anterior and posterior view
Source: Seeley , RR , Stephen , TD , and Tate , P. (1998 ) . Anatomy and
Physiology . 4th ed .
Functions of Skeletal System
• Provide forms: human frame gives shape to the body .
• Support : Bone creation of a body to support the soft tissue and internal
organs . Example : skeletal muscle adhesions .
• Protection : Bones protect the internal organs as important as the brain,
heart and lungs.
• Movement: The bones act as levers during muscle movement .
• The formation of blood cells : bone marrow produces blood cells red blood
cells and white blood cells.
• Storage of minerals : Bone is also a place of storage minerals like calcium
and phosphorus .
Main structures
ligaments
Ligament is an elastic berfiber tissue that connects bone to bone . Among
igament - important for an athlete's ligaments are the anterior and posterior
cruciate ligaments and collateral ligaments in the knee joint.
Figure 3 shows igament -
ligaments in the knee joint
tendons
Tendon is a tissue elastic berfiber not very strong . Tendons attach muscles to
bones and other muscles . When the muscles contract , the tendon at the tip of
the muscles will pull a bone. Some of the strongest tendon is the tendon
Archilles .
Figure 4 shows the tendon on thigh muscles
cartilage
Soft tissue cartilage is strong , elastic and without blood vessels . Cartilage
coating the ends of the bones that make up the joint and serves to protect the
bone from wear smasa going friction between joints. Cartilage also functions as
a shock absorber and are available in various shapes and sizes. Among the most
important for an athlete cartilage is inter - vertebral cartilage in the spine
and cartilage in the knee joint .
Figure 5.1 and 5.2 show the vertebral column of cartilage and cartilage that
covers a bone ends at the knee joint
7.2.2 SYSTEM OF MUSCLE
Studies show material and structural design of rigid joints and cause movement
of support possible. Movement produced by muscle contraction . Also determines
the magnitude of the movement of muscles and movement induced by voluntary or
involuntary nervous system . Muscle not only produces muscle movement but also
has other functions . These muscles are the muscles in order to distinguish
cardiac muscle (heart ) and smooth muscles of the muscles of internal organs
such as the liver and pancreas . Muscles or skeletal frame is also known as
striped muscles .
Main Frame muscles
Major muscles of the body are accustomed to act as agonists or antagonists in
body movements such as kicking, punching, get up , running, jumping and
throwing . Meanwhile, the small muscles that are abundant in the joints will
act as an advocate and a counterweight ( synergistic and stabilizer ) .
Figure 6 shows the major muscles of the body
Muscle function
• Produce Movement: All movements are produced by contraction of skeletal
muscles that act when stimulated by the nervous system . Combination of muscle
interaction allows us to stand , sit , lie down and do other activities
difficult . This contraction happens consciously or controlled ( voluntary ) or
uncontrolled ( involuntary ) . Meanwhile, the speed of contraction depends on the
type of muscle fiber types of fiber whether quick hitch (fast twitch fibers )
or jerk slow fiber type ( slow twitch fibers ) .
• Maintain posture : A combination of muscle interaction not only allows us to
stand , sit or lie down but also helps to maintain body posture . Adhesion of
the muscles to the bones allows posture is maintained. One of the reasons why '
bulges ' is because abdominis muscles are not attached to any other bone of the
factors of overweight or obesity .
• Stabilize Joints : The muscles of the body have different sizes and different
functions. Large muscles such as the quadriceps , triceps , and trapezius
abdominis often act as agonists and antagonists , while the small muscles will
act as a counterweight ( stabilizer ) and supporters ( synergist ) . These
small muscles responsible for stabilizing the joints especially in sports that
require precision behavior or target sports ( sports target ) like archery ,
shooting and ten - pin bowling .
• Produce Heat : Energy is needed to allow the muscles to work . However,
almost 40 % of energy produced turns into heat which increases the temperature
of the external skin or body temperature . Heat - heat produced by the muscles
and removed through evaporation , conduction , radiation and convection to
stabilize body temperature .
Figure 7.1 and 7.2 show the muscles that act as agonist - antagonist and
stabilizer or synergies
7.3 . Exercise Physiology ( 1 hour )
PREPARATION TRAINING
PHYSICAL FITNESS
Physical fitness can be divided into two categories based on health and fitness
fitness -based motor related . Figure 15 shows the components of fitness health
and fitness based on motor related .
Figure 8 components of physical fitness and health -based motor related
7.3.1 The components of health -based fitness
An active man should at least earn a moderate level of fitness in each of the
five components of health -based fitness . These components are :
• Body Composition
Body composition is the relative percentage of fat compared to muscle , bone
and other tissues that make up the body . Body composition in terms of health
fitness, refers to the percentage of body weight consists of fat compared to
fat -free or lean meat . Active individuals have a lower percentage of fat
content , proportional to body weight and height . Individuals who weigh 10 to
20 percent of the standard limit by age, gender and physical considered to have
more weight . Individuals with less fat percentage also is harmful to health .
Weight of an individual can not describe the level of the individual body
composition . This is due to the possibility of someone having a high
percentage of bone weight or have muscle tone . An easy way to estimate the
percentage of body fat a person is by measuring skinfold thickness using
calipers callipers .
• Cardiovascular Resilience
Cardiovascular endurance is keupayaanjantung or cardiorespiratory system to
efficiently pump oxygenated blood throughout the body . Efficient heart allows
us to do continuous work in the long term at a rate of mild or moderate
intensity without feeling tired . Delivery of oxygen-rich blood allows us to
work longer. Those with low cardiovascular endurance is often easily fatigued
and tired . Examples of activities that may increase cardiovascular endurance
is jump rope , swimming, cycling , jogging and aerobics.
• Flexibility
Flexibility means the ability of muscles, ligaments and tenndon allow the body
to move freely in the maximum range of movement . Flexibility can be built through
the stretch. Stretching muscles to do the maximum possible in a mas -term 10 to
30 seconds for each activity. Protrude reach , shoulder stretch , stretch waist
, stretch hamstrings and hips Torque is part of the example aktivitiiaktiviti
flexibility.
Movements in real activity depends on the length of the flexibility of the
muscles, tendons and ligaments and joints form found on parts of the shoulder .
For example , a gymnast has good flexibility .
1 Three types of photo equipment to measure static flexibility ;
(a ) Inclinometer ( b ) Gomiometer ( c ) Flexometer Leighton
• Muscle Strength
Active individuals often have strong muscles to enable the individual to
perform activities that require physical strength . For example , an individual
whose arm muscle strength can throw the ball with a strong inside game of
handball .
Muscular strength is the ability of the intended muscle or group of muscles to
overcome obstacles to the use of force maksim.um . Muscle strength activities
should be carried out systematically and continuously. Muscle strength training
should be done at least three times a week .
• Resilience muscle
A person who has high endurance capable of doing repeatedly and continuously
without feeling fatigue in the long run . For example , running a marathon .
Muscle endurance can be improved through weight training , circuit training and
latihanjeda . Among the activities that can be done for muscle endurance was
lift the heel , push-ups , and lunjur dekam fluctuations bench using his own
body weight as a burden . While activity biceps curl was using the largest
weight load.
7.3.2 Component -based motor related fitness
Athletes involved in competitive sports should be fluent in at least moderate
fitness level in each of the six components of physical fitness that is based
on motor related . Physical fitness components based on motor related stresses
on quality developments that can enhance the performance of the individuals
involved in the sport effectively . Fitness components based on motor related
are :
• Speed
Speed is the ability to perform fast movements . Speeds referred to the
movement distance can be done in minimal time frame . Individuals with foot
speed be able to make a quick run while individuals with hand speed capable of
throwing or hitting a ball with speed.
• Agility
Agility is the ability to change their position quickly and can control the
movement of the entire body . Individuals who agile suitable for boxing ,
gymnastics and football .
• Power
Power is the ability to do activities with maximum force in the shortest period
. Required in the event of power pelurn shot , start sprint , discus , high
jump and long jump .
• Balance
Balance means the retention of an individual's body balance in static and
dynamic position . Among the examples of static balance is handstands in
gymnastics .
• Reaction time
Mernjuk reaction time to the time taken by an individual in response to
stimuli. For example , departing from the starting block as listen to the sound
of gunfire.
7.5 PSYCHOLOGY OF
MOTIVATION
Motivation is defined as the rise in individuals who assist in directing and
maintaining the desired behavior ( Wann , 1997 ) . In this context , the
direction of an individual's actions whether to approach or avoid the
situation. While efforts should refer to the determination of the individual
approaches towards or away from the situation.
Important because it can improve the motivation and initiative spirit athletes
to succeed in sports. Individual participation in sport is influenced by
intrinsic motivation (internal ) and extrinsic motivation (external).
Participation in activities due to interest or fun doing classified as
intrinsic motivation . However, if the participation in the activities of a
desire classified as extrinsic motivation .
MOTIVATION
Intrinsic resources
Involve internal efforts to increase its efficiency self- athletes , improved
performance, fight , compete for success and not influenced by reward or
external influence . Extrinsic sources
Based on external factors such as the desire for materialistic rewards , praise
, honor and truth, or certain awards and encouragement of parents .
7.5.1 Motivation and reward
Extrinsic and intrinsic reward can be positive or negative impact on the
athletes competing in a sports field . A motivated athlete participation
extrinsic reward and at the same time recognized the ability of athletes will
increase the athlete intrinsic motivation . Conversely , if the target of the
extrinsic reward participation or involvement of athletes , but it had not
received the recognition of his ability then this will undermine intrinsic
motivation is an athlete .
Intrinsically motivated individuals who have a thick self-determination .
Participation in the proper things will pertadingan satisfaction and pleasure
in itself . In addition, it can enhance the skills , natural competition in
sports and performance targets .
7.5.2 Skills motivate yourself
In sports, goal adalahrelevan to change behavior. Stimulation of cognitive
behavior need to be made to the behavior of the driver to achieve the goal .
Coaches, athletes and those involved in the field of sports goal setting
techniques to enhance their skills or performance in physical activities and
sports.
Dorothy and Roscue (1995 ) , finds that the goal will stimulate and enhance
ongoing efforts .
7.5.3 Setting goals
The goal is to achieve the planned targets within a certain timeframe . Goal
setting can dikatikan with pemilha method targets within planned. This is a
technique in sports psychology to ensure completeness tasks accomplished. Goal
setting is one of the psychology of effective strategies to improve
performance.
In setting goals, there are three levels of long-term goals , objectives
jangkasederhana and short-term goals .
7.5.4 Long-Term Goals
The long term goal is the final goal of the athlete or team adopt a wonderful
plan for achieving targets. If a long-term goal is difficult to achieve , it is
also the opportunity to make short-term goals and medium-term rmatlamat ement
being implemented as well as the help athletes improve error .
7.5.5 Medium -Term Goals
Medium-term goals set as a guide evaluate the performance of the athlete to
achieve the final goal .
7.5.6 Short -Term Goals
Set short-term goals as a guide to evaluate the performance of athletes in order
to achieve long-term goals . Short-term goals are usually set daily and weekly
. Performance has been achieved in the short-term goals can merangsagkan
athletes to improve performance and achieve long-term goals .
Setting goals to increase athlete motivation to not give up easily with their
achievement and strive to improve performance and help assess the effectiveness
of the program.
7.5.7 stimulus words themselves
Stimulus words themselves is one of the cognitive strategies that can convince
individuals to achieve the desired performance . Words that also help achieve
excellence in training and competition .
Word or words can boost existed in various forms and is used in different
situations . In this context , the words of self- help athletes learn stimulus
kamahiran , fix mistakes , ready for the competition, focus attention , create
a good emotion to compete , build confidence and improve efficiency.
CONCERNS
The concept concerns
Anxiety can be defined as the cognitive or emotional effects resulting from the
perception of the situation at hand. It is born in the form of a threat to be
received by an individual as defeat , physical intimidation and embarrassment (
Shaharudin , 2001)
According to Weinberg and Could (1999 ) , anxiety is a negative emotional state
, include restlessness and anxiety associated with the activity of a person in
a field . Normally, the situation is not fixed and concerns changing .
Setap individuals will experience different levels of anxiety in certain
situations . Anxiety can interfere with concentration and even athletes are
able to affect the pattern of presentation and their performance in
competitions participated. During the contest , feelings of anxiety experienced
by athletes not only themselves, but also experienced by coaches , supporters
and spectators.
There are two types of anxiety trait anxiety and anxiety while.
• trait anxiety
Trait anxiety refers to individual personality characteristics that tend to see
situations as threatening . Those who suffer from anxiety trait will respond to
situations at different levels of intensity of concern .
For example , two hockey players who were given a penalty shot at the end. They
have a skill level that is equal but have different levels of anxiety due to
the atmosphere of their personality . Perna in A has a low level of trait
anxiety will consider a penalty shot is not something threatening . Instead
Player B tretnya anxiety levels high , consider taking a penalty stroke as
something threatening .
7.6. SAFETY , SPORTS INJURIES
Sport is a vigorous physical activity that exposes athletes to a high risk of
injury if safety precautions are not given priority. Therefore, the security
aspects should be given priority in order to reduce the risk of injury and to
ensure athletes are at a higher level of fitness without a long break due to
injury.
SPORTS SAFETY 7.6.1
In preventing injuries and accidents from occurring and to ensure that athletes
train and compete in a safe environment , some security measures in the following
aspects should be considered.
Sports Equipment and Facilities
The equipment used should be appropriate to the age, height , size and physical
skills as well as provide comfort to individuals who menggunakannya.Peralatan -
sports equipment such as hockey sticks , tennis rackets or badminton , football
shoes and ball size used should correspond to the age and size athletes. All
equipment including gym equipment and sports facilities such as tennis and golf
used to be in a safe condition . Review and inspection of the facilities and
equipment used to do from time to time to ensure that aspects and features of
security and authority.
Safety Equipment
All players must wear safety equipment during sports . Examples of this
equipment is intended shin pads protect the tibia hockey and football players ,
abdominal guard that protects the stomach combat sports athletes , and face
protection for catchers in the game of softball players . The design of this
equipment is to prevent injury to the structures of our high-risk anatomy .
clothing
Sports clothing should be comfortable and fit your body size . Clothing is made
from cotton is the most suitable for the hot weather of our country because
this material allows sweat absorbed and evaporated . Assist in controlling this
situation and prevent an increase in body temperature. Tights are popular today
, such as tights help maintain muscle temperature at optimumtetapi level we
need to ensure that not too tight to disrupt blood flow and cause a sense of
discomfort during activities .
competition rules
Ages sports competition organizers should prioritize safety, particularly in
the listing rules of certain tournaments . For example , touch rugby players do
not allow the tackle . Cricket deer using only a soft rubber ball . Nor
gymnastics involves motion of the front and back somersaults for participants
aged 6-10 years . Competition rules of a game are aspects that can be adjusted
according to the conditions for giving priority to safety aspects .
Warm-up activities
Warm-up activity is the earliest steps to avoid sports injuries . It's
important to warm up before you start doing any physical activity or
competition as beneficial to mental checkers physical preparation of athletes.
Among the purposes warm up is to increase body temperature and the temperature
of the muscles. By doing this activity in muscle tension decreases to make the
muscles relax condition . This situation facilitates the movement of explosive
, such as kicking the ball and sprint belari . Actions involved in the
contraction of large muscle groups a short period, was followed by the maximum
stretch these muscles .
Warm-up activities to increase the intensity of the movement and also to
facilitate adaptation of the heart, lungs and blood vessels to increase the
pace of work occurring during sports. This adjustment process to reduce stress
( Stress ) on physiological metabolism involving structures in detail.
Enzymatic reaction is also accelerated when high body temperature . This condition
can delay the formation of lactic acid in the blood.
Psychological aspects , athletes do enough warm-up usually feel more confident
when they wanted to compete . During competition , athletes will have the
opportunity to do rehearsals before performing movements in real situations .
cooling off
Aktiviiti cool the body seeks to restore normal physiological function to the
progressive Scara . Cool-down process involves two main phases , namely slack
and low intensity activities . Activities This stretch during menyajukkan body
to reduce muscle fatigue and also improve the flexibility of muscles, tendons
and ligaments. This is because the internal temperature is high immediately
after physical activity .
Cool-down activities also help accelerate blood circulation to the heart ,
restoring blood pumped by the heart to the tip of the body such as the feet and
hands after playing . If an athlete stops immediately after a session of
high-intensity activity , blood collection (blood Pooling ) is formed on the muscular
system . This situation can lower blood pressure and mengakibatnya athletes
feel dizzy , nauseous or It might faint.
SPORTS INJURIES 7.6.2
In addition to physiological trauma that has been explained , the physical
injuries are common incidents occur , especially in athletes who have achieved
high performance . Level athletes are more prone to physical injury . It is
because of the training they do is high intensity . Strong physical
modification program is a major step to minimize the risk of this injury .
Some common physical injuries are:
• soft tissue injuries
Soft tissues of the body include the skin , blood vessels , nerves, muscles,
tendons, ligaments , and glands lining protects the organs in the body . Muscle
cramps are the pain inflicted on the large muscles . This situation caused the
mechanism of muscle contraction agonist - antigonis are not in line and place
in a long time . The main factors that cause dehydration cramps , chronic
fatigue and shock or blow on the muscles .
Muscle spasms can be overcome by doing static stretching . If pain persists,
stop stretching and end treatment for muscle activity may be other injuries as
a result of complications.
• Muscle tension
Muscle strains occur when the fiber - fiber muscle injury. Muscle tension is
the result of a physical mechanism to protect the muscles from a chronic injury
. Hamstring muscles are the muscles that often experience cramps .
Tension usually involves tearing the muscle fibers . Mild muscle tension
resulting in extreme pain if continued to be active . Kettegangan more serious
can cause bleeding in that we did not get menggaerakkan the member is stressed
.
• Muscle aches
Muscle aches are a common phenomenon experienced if we do high intensity
physical activity when fitness levels are still low . Kencederungan
experiencing muscle aches directly proportional to the age factor . Menifestasi
muscle aches are unbearable pain , followed by fatigue. This situation can be
experienced just physical activity . Salit feel this can be delayed until after
12 hours of physical activity .
Muscle aches occur due to tiny tears in the muscle fibers , and as a side due
to lack of oxygen supply to the muscles during activity . These injuries can be
avoided by doing activities at the appropriate intensity level of our fitness .
• Cuts
May involve injury at the outer skin and the ( sliced or cut by broken bones
) skin . The type of lesion consists of abrasion ( scratch on the surface of
the skin ) pieces ( contact with sharp objects ) and perforations ( punctured
by sharp objects such as nails ) are in and puncture wounds can result in
serious damage to the blood vessels . Observations on current security measures
activity is the best way to protect yourself from injury.
• Bruising due kontusi
Kontusi refers to stamping directly on the outer surface of the object or limb
tissue . If a strong shock , blood vessels can rupture and blow the place of
accumulated blood . Dark blue color is formed in the skin as a sign of bleeding
in the place.
If the same place repeatedly received shock , marking the calcium will be
formed in the area. Structural members involved later mengalamui difficulty
moving . Kontusi an effective method of prevention is in protecting high-risk
parts to use as disiku and knee pads .
• Hard tissue injuries
Hard tissue involving all the bones and joints of the body . Bone fractures are
usually caused by high stress suffered bone . Long bones , such as the humerus
and femur can take about 6 weeks to heal from a fracture . Meanwhile rulang
small - bone requires a period of 3-4 weeks to heal . Cement method is the
common treatment techniques to prevent mobility in bone fracture. Once the
cement or plaster treatment ended , the bone has healed isometric weight
training should be applied for the purpose of rehabilitation.
• dislocation
Dislocation occurs when the ends of the bones that form the joint disconnected
or out of place lekatannya . Soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments , tendons
and blood vessels injured when dislocation occurs . These injuries often occur
in the shoulder joint . Rest actively encouraged for athletes who are injured .
High level of fitness and technical mastery of skills is the method most
effective dislocation prevention .
• head injury
Concussion occurs when a blow on the athletes this kepala.kecederaan cause
brain trauma and coma for chronic cases . Concussion usually occurs in contact
sports such as rugby , football , boxing and combat sports .
Athletes who suffer concussion usually exhibit symptoms of nausea and loss of
balance while. In some cases, amnesia (loss of memory ) can occur for a short
period . Besides fainting, physical signs of concussion usually not noticeable
and the victim should be referred to a physician immediately. Athletes who
suffer concussion must be sidelined for a specific period set on the advice of
a physician.
Concussion, also classed as an accident. Therefore, the maximum attention to
safety measures during exercise are the most effective preventive measure .
7.6.3 INJURY MANAGEMENT AND HELP START
All sports injuries occur during competition or training must be dealt with
immediately . ability of the athlete to continue training or playing just
suffered an injury should be referred to a physician. Among the methods of
managing and evaluating sports injuries can be performed without a physician is
TOTAPS , DR . ABC and RICE
• RICE
RICE acronym refers to the words rest , ice , compression and elavation . The
table below shows the meaning of RICE in the context of injury management. Rice
first aid method is intended to :
• prevent other soft tissues from injury.
• Reduce pain.
• Reduce swelling .
• Maintaining fitness while treating the injured .
• Restoring confidence to the injured victim .
• Prevent recurrence of the same injury .
RICE is suitable for the management of sports injuries such as sprains ,
dislocations , bumps , sore , cracked and kontusi , tension and muscle spasm .
The injured athlete should be sidelined . Any movement will result in place of
the injured or sustained increase in blood circulation and this will make
things worse injuries.
Ice wrapped in cloth or plastic didemah over the injured area . Injuries that
do not involve an open wound should be prescribed this treatment . Do not allow
the use of ice directly on the injured area as it will result in ice -burn and
turn off the cells around the injured area . Ice Demahan help to lower the
temperature of tissues and cells that have suffered kecederan and can restore
damaged cells faster.
The injured part should be wrapped to prevent excessive swelling .
Elevate the injured area for the purpose of facilitating and merpecepatkan
return blood to the heart. This will reduce the bleeding of the injured . Lika
parts should be higher than the heart .
All first aid treatment and explained this is effective for a period of 48
hours after injury athletes. However, physicians should reference delay. In
that time period , the athletes are not encouraged to undergo sports massage
because massage process potentially pose complications to the kecedeaan . The
processes involved in injury therapy is usually done after being given
permission by a physician .
SPORTS INJURY THERAPY 7.6.4
Rehabilitation or restoration of injured athletes usually run by a
physiotherapist on physician instructions . Injuries suffered chronic joint and
muscle can not be restored through rest alone . Manjalankan injured athletes
need treatment or rehabilitation to restore the function of the injured part to
its original condition . Among the functions of rehabilitation are:
a) Strengthen the muscles, ligaments and tendons that have been recovered from
the injury.
b ) Restoring the athlete 's fitness level to its original condition .
c ) Increase the range of movement of joints and muscles 's stability .
d ) Restoring confidence in his ability athletes .
Physiotherapy is the treatment carried out by a trained physiotherapist in the
direction of a physician. The main objective of a trained physiotherapist on
physician instructions . The main objective is to help mempecepatkan sports
physiotherapy healing rate of a sports injury . The goal of physiotherapy is to
process
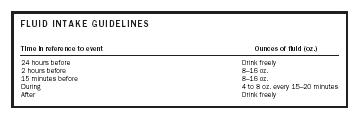
REQUIREMENTS 7.6.5 LIQUID
Fluid loss from the body ( dehydration ) occurs through 2-3 liters of
sweat per hour , if the high intensity sport activities and lasting done.
An athlete should drink water before , during and after sports
activities. Cold water is the best fluid to drink. Heat generated ( through
sports ) of muscle carbohydrate and fat metabolism for energy m'hasilkan .
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
Water loss will be critical if not replaced .
Athletes lose 8-12 % of their body weight when performing physical
activities in hot and humid weather conditions ( humid ) .
Water loss causes blood plasma volume reduction . Electrolyte ( ion
Na + and CI ) that control the water content in the body ( extracellular ) .
Blood pressure drops when the water content in the blood plasma down .
Heart has to pump blood more often and faster to maintain cardiac output
- essential to ensure continuous supply of blood to the muscles .
The reduction in blood flow will occur because blood is needed to supply
nutrients and oxygen to the muscles. This can cause the body temperature rises
and the resulting thermal stress .
Heat stress ( Heat Stress )
Main factors : Exposure to the sun and humid weather ( humid ) levels.
( i ) muscle cramps ( muscle cramp )
- Occurs in gastrocnemius and rectus abdominis .
- Related to the water and electrolyte imbalance
in the body .
( ii ) Loss of excess water ( heat exhaustion ) .
• Through perspiration and not replaced may result seseorag fell down .
• Due to lack of quantity of electrolytes such as sodium ( Na + ) and chloride
( Cl- ) .
• Drinking plenty of water and rest in a cool area . If left untreated, can
lead to heat stroke.
Heat stroke ( Heat Stroke )
Can be fatal if not treated immediately .
Cause: Unknown.
Features: fainting , dry skin , increased body temperature to 41 ° C.
Effects : central nervous system disorders .
Can change suddenly without warning.
Treatment should be done within 45 minutes after suffering a heat stroke.
Treatment should be done within 45 minutes after suffering a heat stroke.
Priority to lower the temperature of the victims :
• Remove all clothing from the victim .
• Pour cold water over her body and kipaskan victim.
• Send the victim to the hospital.
• Patients may be given a drink tidakk directly .
• Grant liquid only via intravenous drip " right away.
Table 6 : Measures to avoid heat stroke
step
Avoid heat stroke
Adapt to the hot weather and temperatures .
At least 1 week before the competition
Drink plenty of water before , during and after a training session @ the
competition.
Cold water - liquids to drink. Isotonic drinks also should be able to be taken
.
Wearing clothes made of suitable materials .
Specifically for use in hot weather .
Avoid training in hot weather . Time between 11:00 to 4:00 pm is the hottest
period . If must practice , should be done in the hall.
![When the body is dehydrated, blood circulation decreases and the muscles do not receive enough oxygen for maximum performance. Thirst is an indication that dehydration has already occurred, so it is important to drink frequently during exercise, before thirst sets in. Here, Sean "P. Diddy" Combs drinks from a water bottle during the 2003 New York City Marathon. [Photograph by Richard Cohen. Corbis. Reproduced by permission.]](http://www.faqs.org/nutrition/images/nwaz_02_img0222.jpg)